Course Introduction:
Econ 3391
Prof. Richard Sweeney
Course website:
http://www.richard-sweeney.com/econ3391/
Slides for today:
https://www.richard-sweeney.com/econ3391/extras/IntroLecture/Intro.html
Outline for today
- Energy is economically important
- Energy markets are economically inefficient
- This course: Using economics to help power growth without destroying the planet
- Course logistics
Energy is important




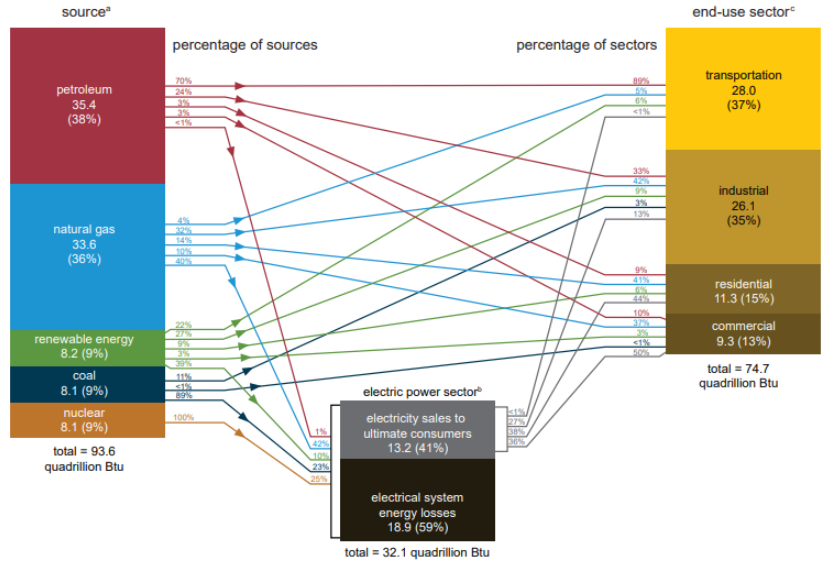
Energy growth and economic growth
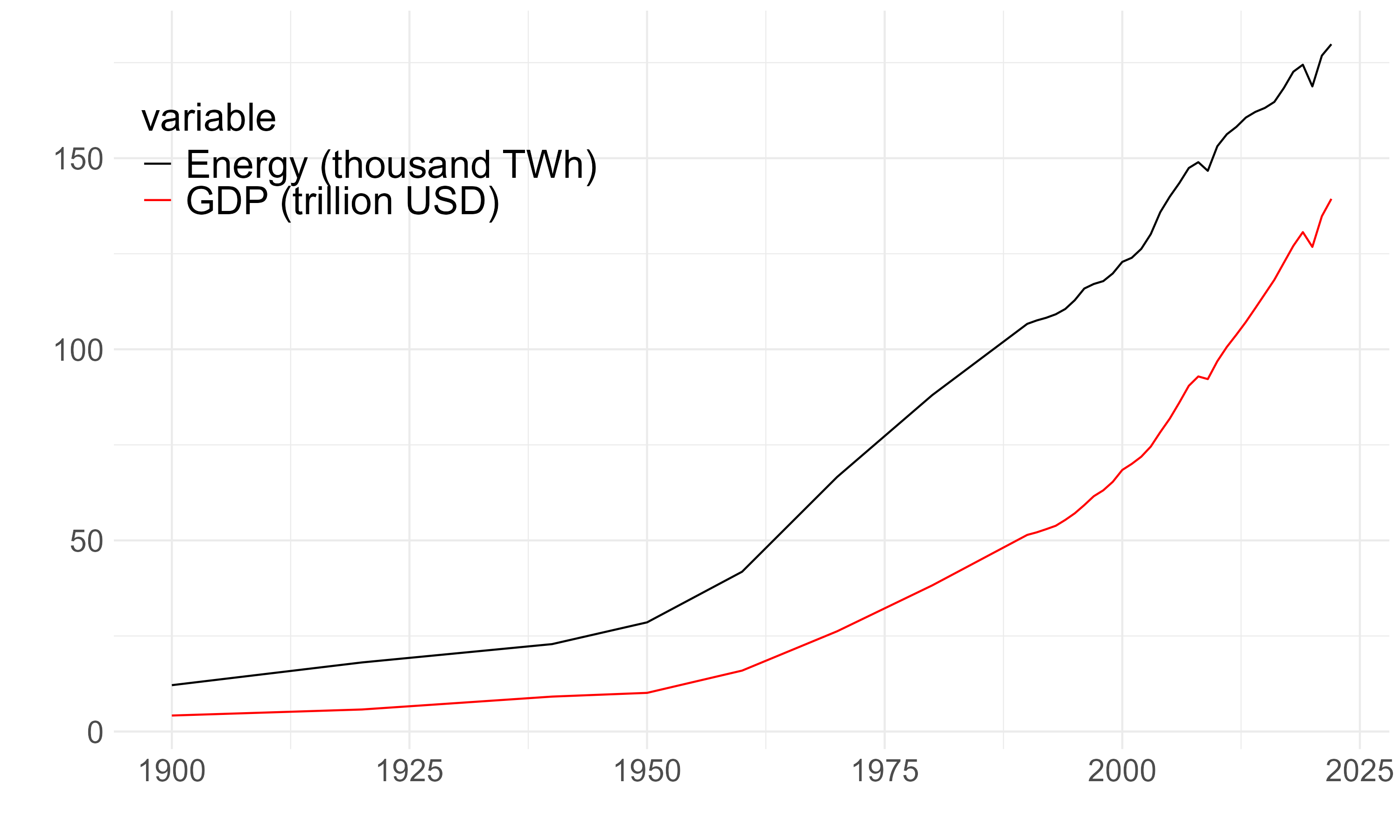
New challenge: AI
AI will require incredible amount of energy
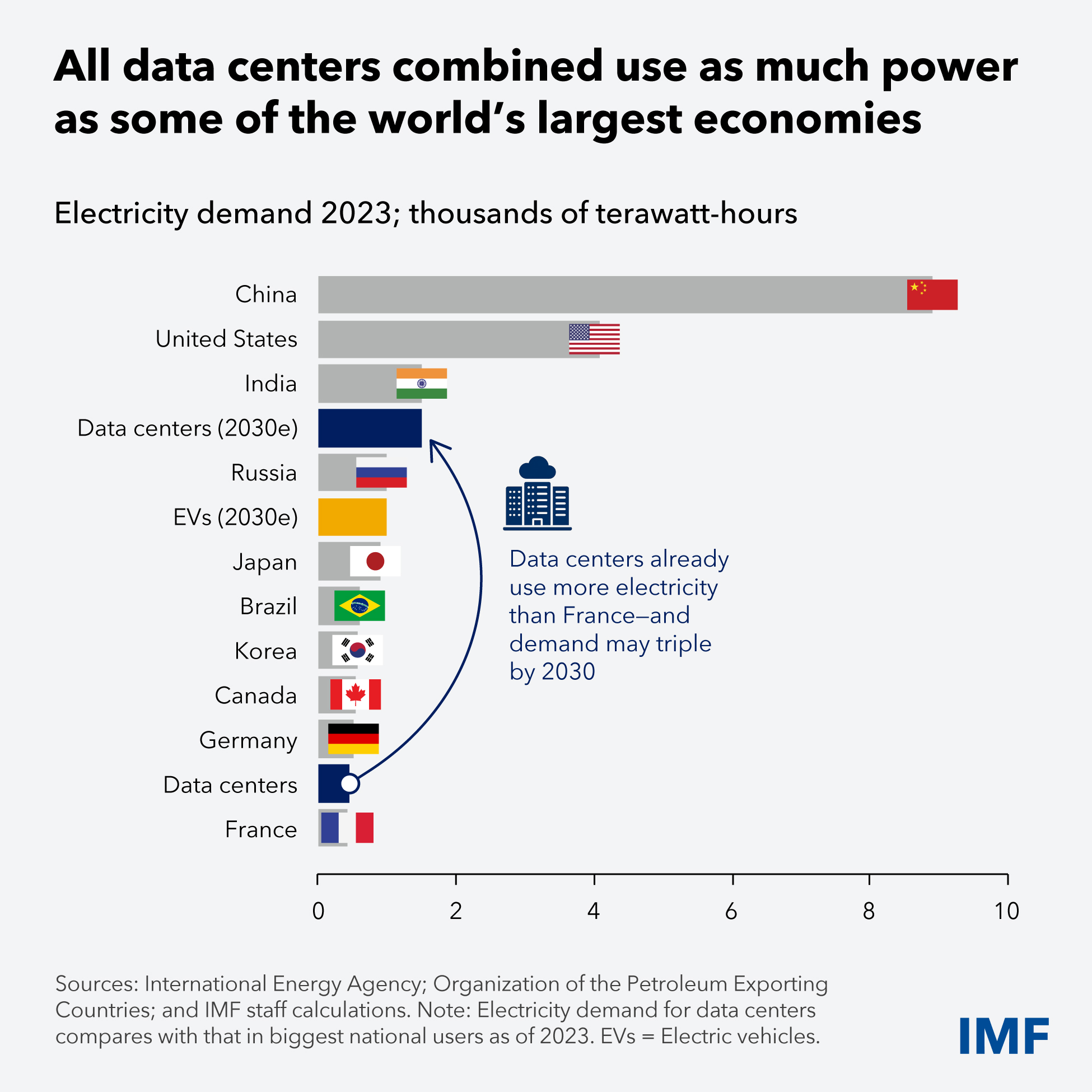
This is already driving up prices
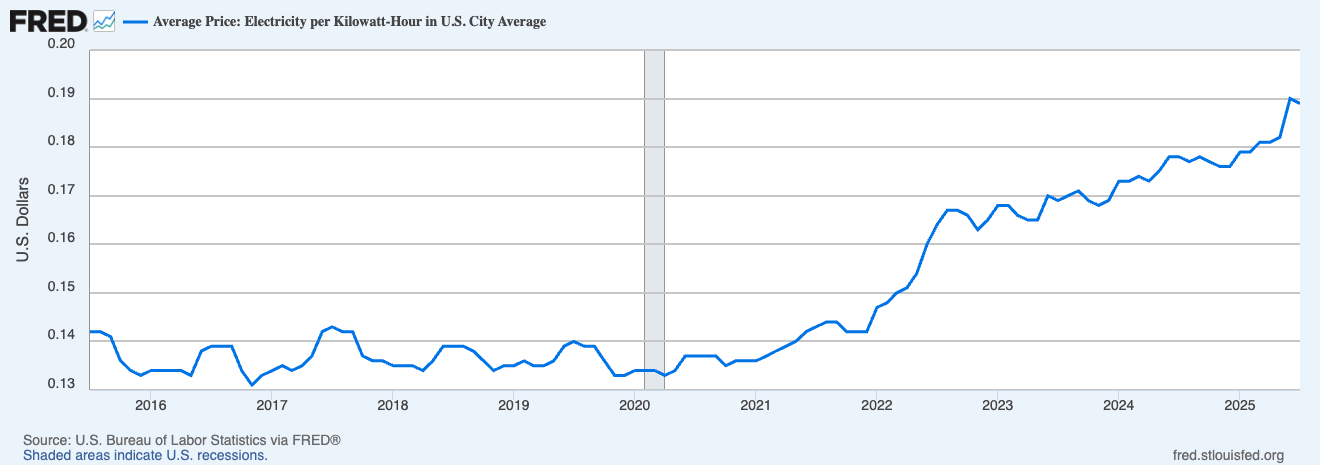
Core policy goal: Ensure cheap, reliable energy necessary for 21st century economy
Problem: Our current energy mix is unsustainable (and economically inefficient)
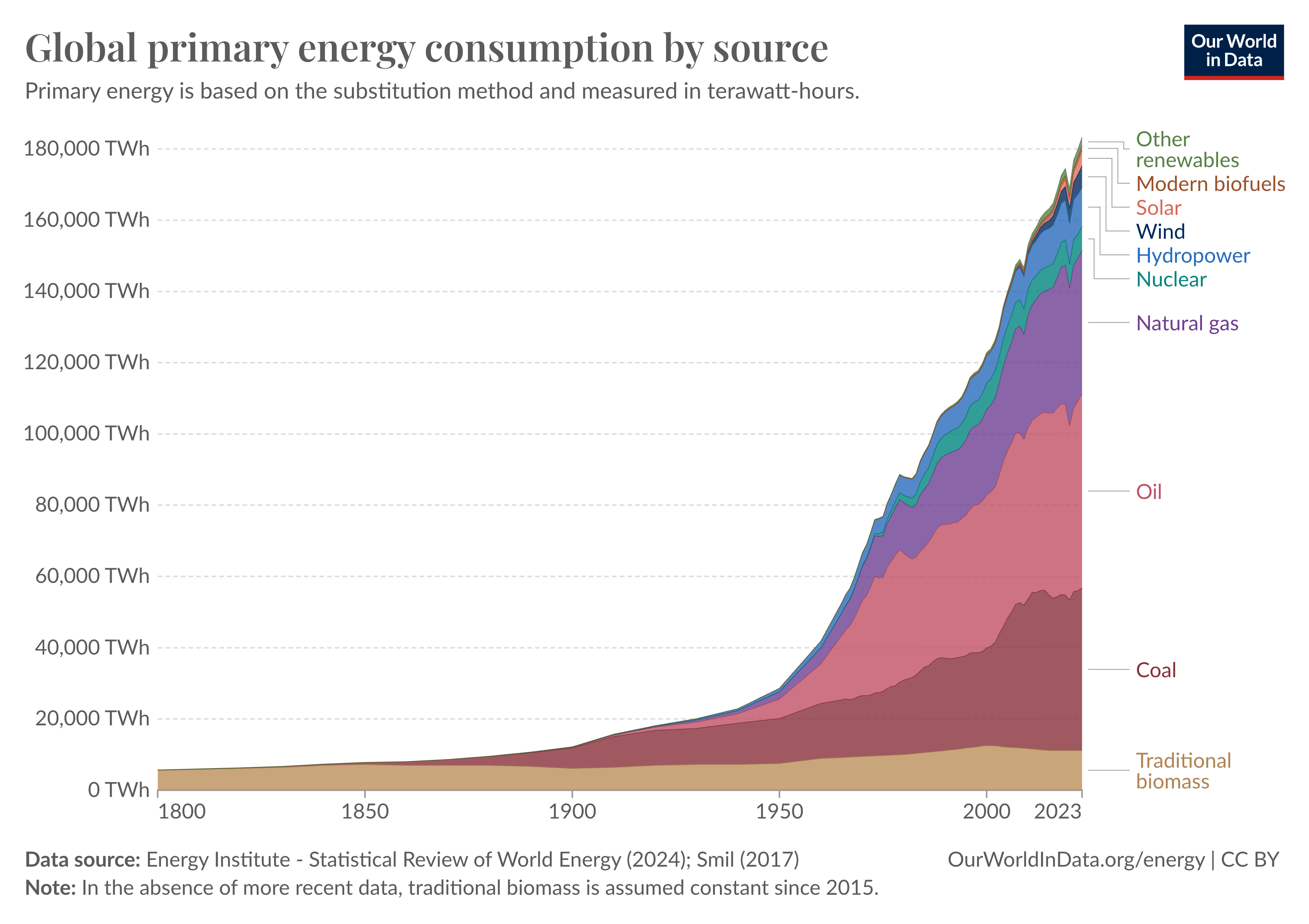
Where we get our energy from
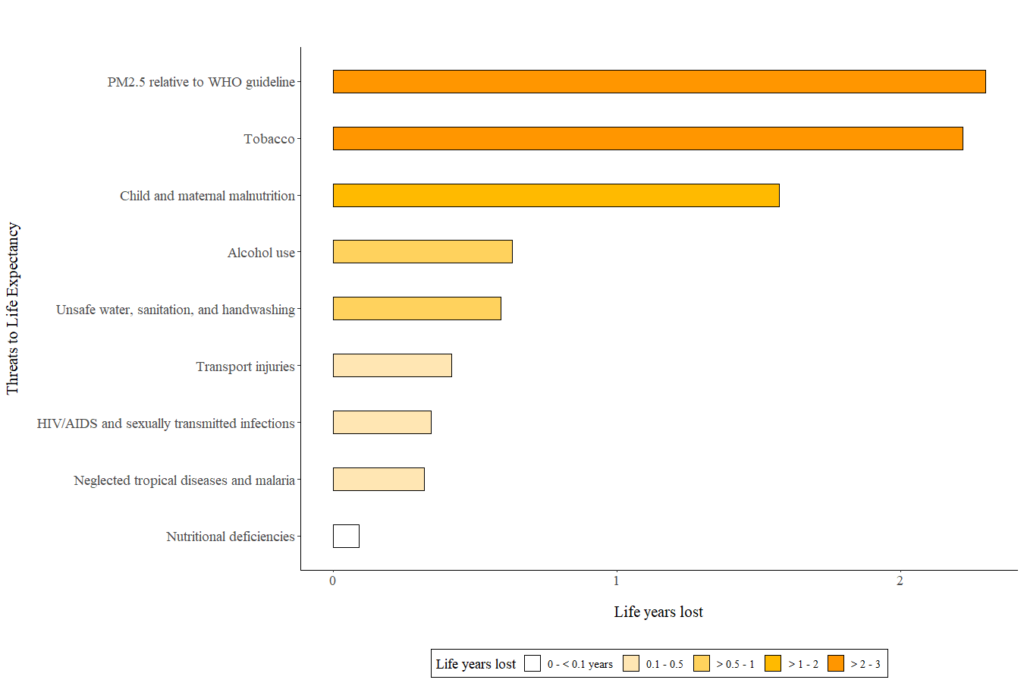
Energy use is associated with many negative externalities
An externality exists when the consumption or production choices of one person or firm enter the utility or production function of another entity without that entity’s permission or compensation.
(more on this in two weeks)
Pollution from energy is a leading cause of death worldwide
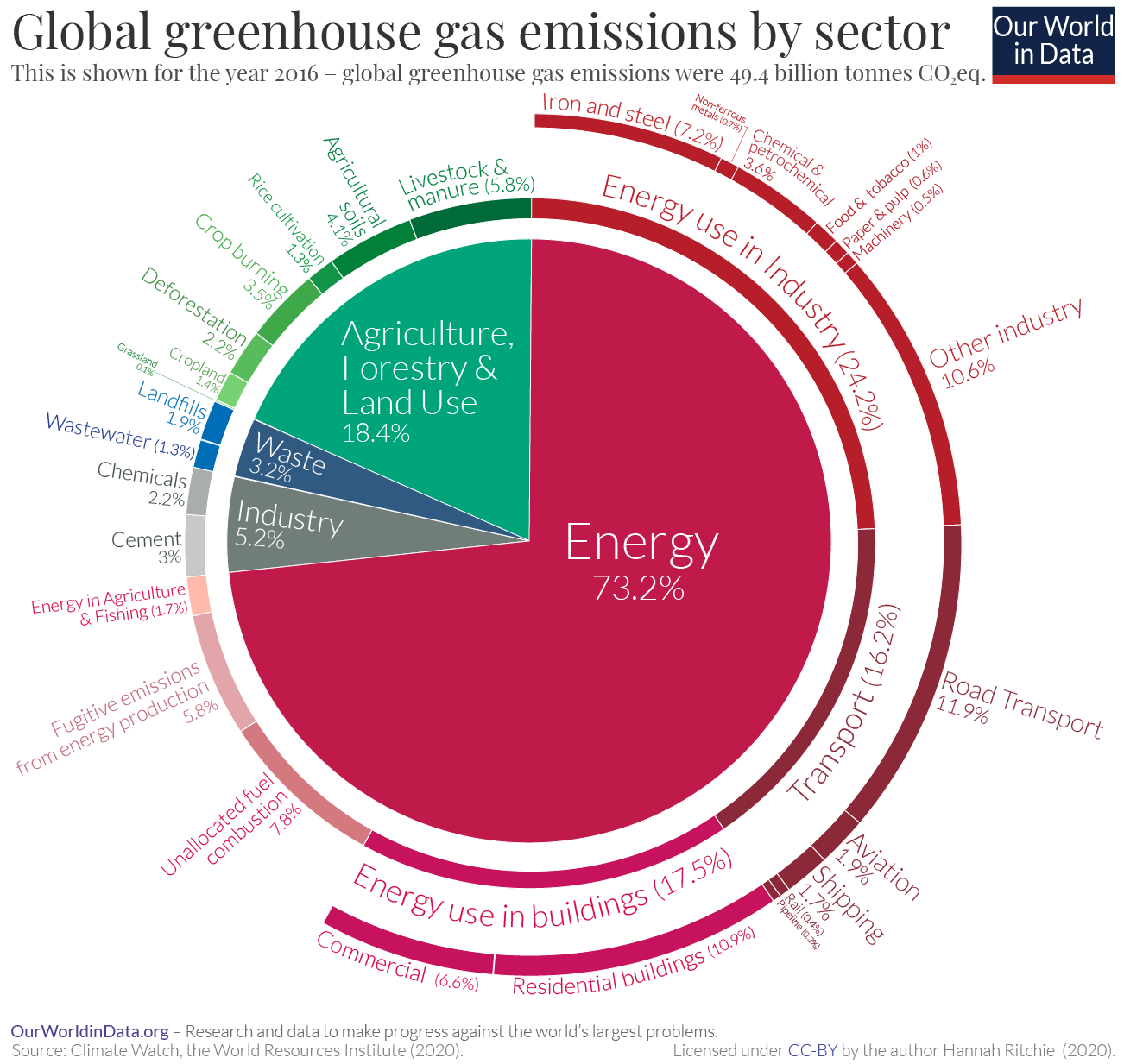
Going forward the biggest challenge is climate change
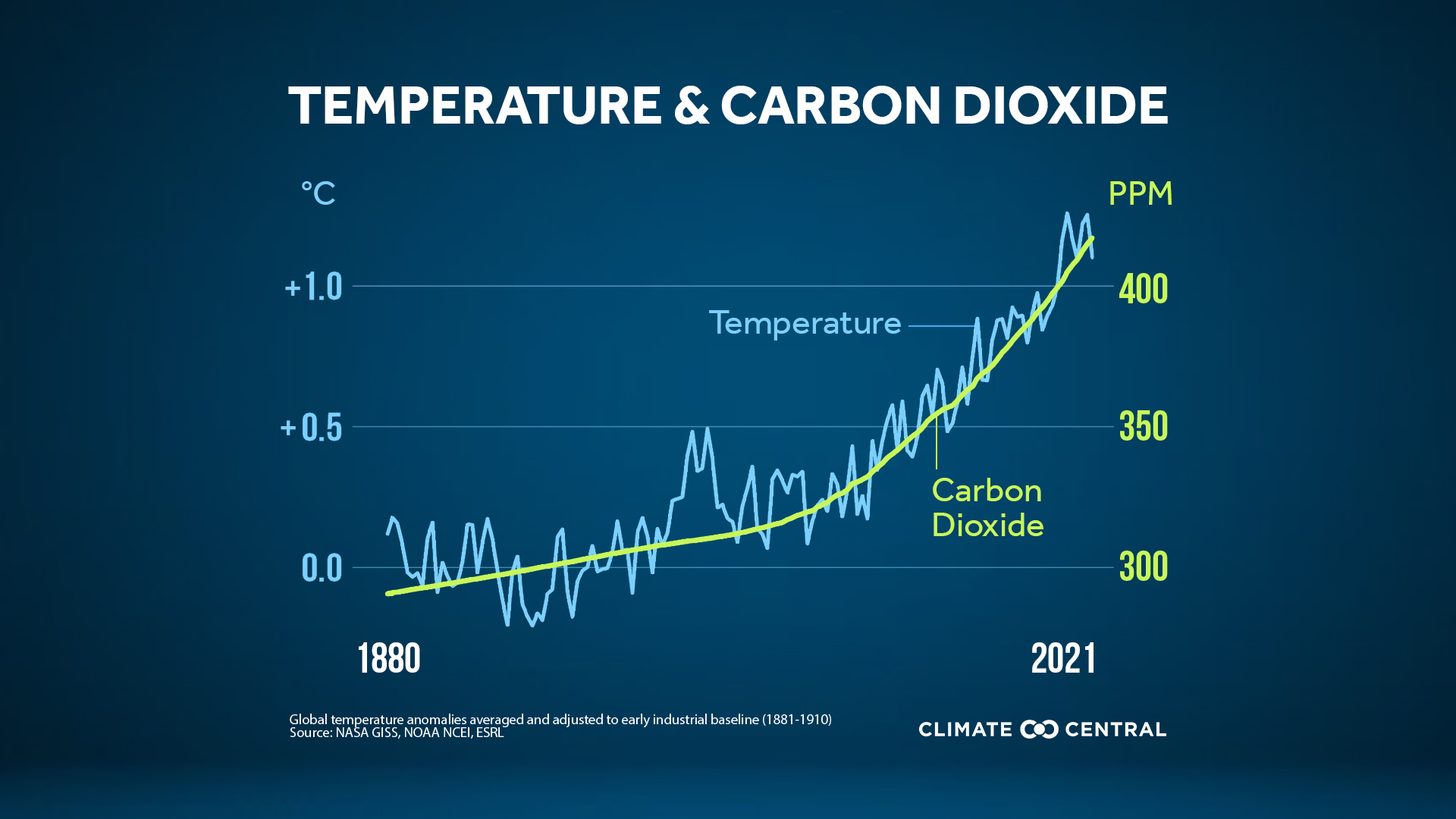
Need abrupt action to avoid things getting much worse
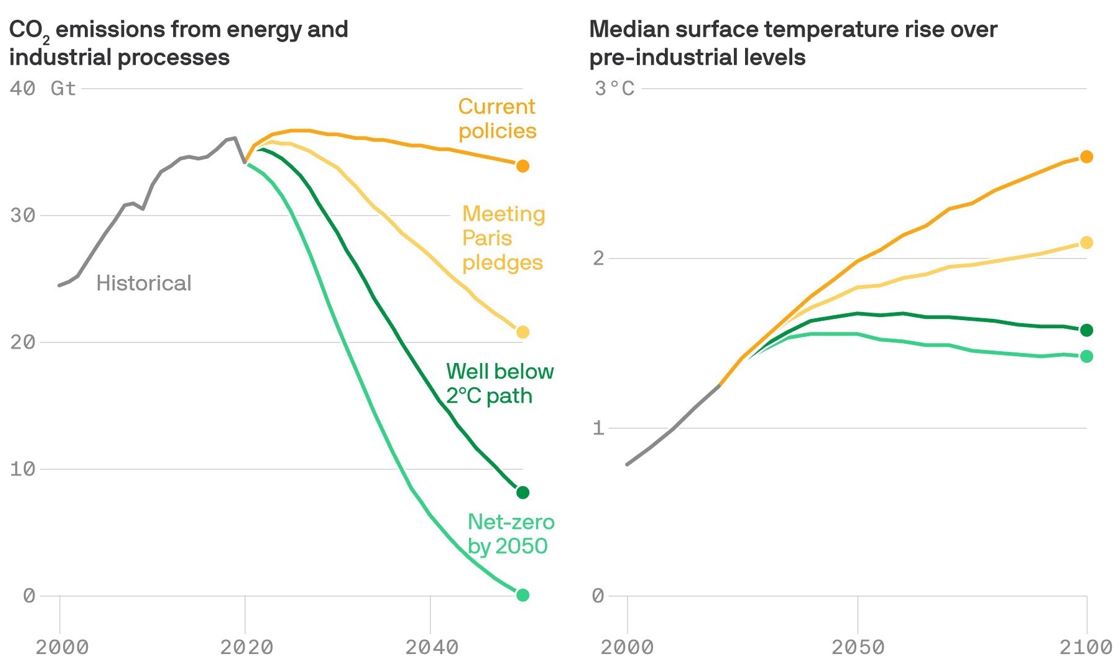
Source: Axios
Good News: Basic outline of a solution is clear
- 75% of global CO2 emissions come from energy
- Other big sources are deforestation and industrial production (like cement and steel)
Step 1: Electrify everything
- Switch essentially all energy use to electric power
- heating, transportation (!)
Step 2: Decarbonize electricity production ASAP
- Shut down coal plants [carbon capture and storage]
- Switch to wind and (mainly) solar
- Increase energy efficiency of durables (ACs, water heaters, etc)
We will focus on the economics of the energy transition
- Basic engineering / technical aspects of the problem are well known.
- The main challenges are economical and political
- We need to move away from fossil fuels
- How much to decarbonize?
- How quickly?
- How to get there?
Key insight of economics is that we want to maximize net benefits
Course overview
Goal 1 of the class: Learn how to apply econ toolkit to an important policy problem
- Econ is the study of how to “best” allocate scarce resources
- There are tradeoffs! Want to max net benefits
- Think on the margin
- Use economic models to predict and understand human behavior
- Use incentives (ie prices) rather than bans
- Market power: firm’s don’t always behave as we’d want them to
Goal 2: Teach you about energy markets
- Energy markets have some unique features that make them different from other markets
- Understanding these features is essential for applying economics to energy and environmental policy
- We’ll go over basic energy terminology and concepts over the course of the semester
- Useful for those of you who want to work in the energy sector
AI has changed the way I approach this course
- Previously more focused on problem sets, applying econometrics and project work
- This year I’m assuming that the way that you all use AI makes those exercises less useful (and uninformative for grading)
- Instead, I’m focusing more on in-class activities and discussion
- Idea is to hone the skills that are actually valuable in today’s AI powered work place
- Critical thinking and ability to apply econ concepts
Syllabus
Up next: Electricity markets
Prior to next class (Thursday):
- Watch “How does the power grid work?”
- Watch this short video on California’s ISO (the market we’ll be looking at in the game).
- Watch this short video lecture on how a uniform price electricity auction works.
- Read the Energy Market Game About page and player tutorial.
- We’ll be starting an Energy Market Game.
- Groups will be assigned Thursday.
Econ 3391 - Intro